Abstract
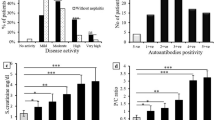
Previously it has been suggested that the presence of antibodies against dsDNA of the IgA class may define a subset of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients suffering from nephritis and arthritis. Therefore, these autoantibodies were measured in sera of 352 patients with SLE, 81 blood donors, and 189 patients with rheumatoid arthritis using a new ELISA based on human recombinant dsDNA as antigen. IgA anti-dsDNA antibodies were found in 19.9% of the sera from patients with SLE, but in none of the sera from 81 normal controls and 189 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The association of these autoantibodies with 31 clinical and 36 laboratory parameters was calculated. IgA anti-dsDNA antibodies were found to be associated with parameters of disease activity such as elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and consumption of complement component C3, and the clinical parameters vasculitis, acral necrosis and erythema, but not with nephritis and arthritis. Therefore, IgA anti-dsDNA antibodies define a subset of SLE patients, and monitoring of IgA anti-dsDNA antibodies may be helpful as a prognostic parameter in patients with SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Additional information
Received: 12 April 1998 / Accepted: 24 April 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witte, T., Hartung, K., Matthias, T. et al. Association of IgA anti-dsDNA antibodies with vasculitis and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology International 18, 63–69 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002960050059
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002960050059