Abstract
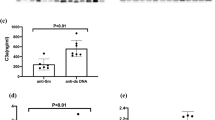
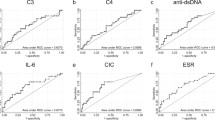
The objective of this study was to assess the utility of measurement of thrombomodulin, antinucleosome antibodies, sVCAM-1, sICAM-1, neopterin, fas ligand, IL-10 and sIL-2R in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to compare them with traditional markers of SLE activity (anti-dsDNA antibodies, C3, C4) and the ECLAM index of disease activity. The measurement was performed over a 6-month period at three consecutive time points after 3 months in each of the 52 patients with SLE. Anti-dsDNA antibodies, thrombomodulin, antinucleosome antibodies, sVCAM-1m sICAM-1, neopterin, fas ligand, IL-10 and sIL-2R were tested by ELISA technique, while C3, C4 components of complement were tested by nephelometry. Fas ligand and IL-10 did not correlate with the ECLAM index. The rest of the markers showed significant correlation with the disease activity index. Thrombomodulin and anti-dsDNA antibodies reflect in the best way the changing trend in disease activity. Antinucleosome antibodies seem to be a promising marker useful in early diagnosis. Soluble VCAM-1, sICAM-1, neopterin and sIL-2R are interesting molecules with a role in disease pathogenesis, but their practical utility is limited.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 September 2000 / Accepted: 31 March 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horák, P., Ščudla, V., Heřmanová, Z. et al. Clinical Utility of Selected Disease Activity Markers in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 20, 337–344 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100670170023
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100670170023