Abstract
Benlysta (belimumab) is a fully human recombinant monoclonal IgG antibody that neutralizes soluble B-lymphocyte stimulator and inhibits its biologic activity. Benlysta was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The current review discusses the data from the belimumab clinical trials and the role of this new medication in the treatment of SLE. We propose that Benlysta should be used in antinuclear antibody–positive patients with active disease in whom the goal of therapy is to decrease SLE activity, reduce flares, and help lower background medications. With this being the first drug approved for treatment of SLE in 50 years, patients have more treatment options, while researchers have a greater understanding of SLE and clinical trial design in such a heterogeneous disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Urowitz M, Gladman D, Ibanez D, et al. Evolution of disease burden over 5 years in a multicentre inception SLE cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011.
Lim SS, Drenkard C, McCune WJ, et al. Population-based lupus registries: advancing our epidemiologic understanding. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(10):1462–6.
Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(9):1725.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25(11):1271–7.
Egner W. The use of laboratory tests in the diagnosis of SLE. J Clin Pathol. 2000;53(6):424–32.
ter Borg EJ, Horst G, Hummel EJ, et al. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(5):634–43.
Askanase AD, Wallace DJ, Weisman MH, et al. Use of pharmacogenetics, enzymatic phenotyping, and metabolite monitoring to guide treatment with azathioprine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(1):89–95.
Carneiro JR, Sato EI. Double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial of methotrexate in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1999;26(6):1275–9.
Ginzler EM, Dooley MA, Aranow C, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(21):2219–28.
Baker KP, Edwards BM, Main SH, et al. Generation and characterization of LymphoStat-B, a human monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the bioactivities of B lymphocyte stimulator. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(11):3253–65.
Nashi E, Wang Y, Diamond B. The role of B cells in lupus pathogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(4):543–50.
Gross JA, Johnston J, Mudri S, et al. TACI and BCMA are receptors for a TNF homologue implicated in B-cell autoimmune disease. Nature. 2000;404(6781):995–9.
Moore PA, Belvedere O, Orr A, et al. BLyS: member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science. 1999;285(5425):260–3.
Thompson JS, Bixler SA, Qian F, et al. BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically interacts with BAFF. Science. 2001;293(5537):2108–11.
Zhang J, Roschke V, Baker KP, et al. Cutting edge: a role for B lymphocyte stimulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2001;166(1):6–10.
Petri M, Stohl W, Chatham W, et al. Association of plasma B lymphocyte stimulator levels and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(8):2453–9.
Furie R, Stohl W, Ginzler EM, et al. Biologic activity and safety of belimumab, a neutralizing anti-B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) monoclonal antibody: a phase I trial in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(5):R109.
Wallace DJ, Stohl W, Furie RA, et al. A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(9):1168–78.
Furie RA, Petri MA, Wallace DJ, et al. Novel evidence-based systemic lupus erythematosus responder index. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(9):1143–51.
Jacobi AM, Huang W, Wang T, et al. Effect of long-term belimumab treatment on B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: extension of a phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(1):201–10.
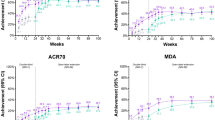
• Furie R, Petri M, Zamani O, et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(12):3918–30. This publication describes results of one of the phase 3, international, randomized controlled clinical trials of belimumab plus standard of care in active SLE patients. This study met its primary end point, showing efficacy of belimumab at 52 weeks using the SRI. It was also shown that the rates of AEs, serious AEs, and infections in the belimumab groups were not significantly different from those of the placebo group.
• Navarra SV, Guzman RM, Gallacher AE, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9767):721–31. This publication describes results of one of the phase 3, international, randomized controlled clinical trials of belimumab plus standard of care in active SLE patients. This study met its primary end point, showing efficacy of belimumab at 52 weeks using the SRI. It was also shown that the rates of AEs, serious AEs, and infections in the belimumab groups were not significantly different from those of the placebo group.
Stohl W, Hiepe F, Latinis KM, et al. Belimumab reduces autoantibodies, normalizes low complement, and reduces select B-cell populations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2012.
van Vollenhoven RF, Petri MA, Cervera R, et al. Belimumab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: high disease activity predictors of response. Ann Rheum Dis 2012.
• Chowdhury BA. FDA briefing information BLA 125370; Benlysta (belimumab), A.A. Committee, Editor. 2010. This publication describes and summarizes the safety of all the belimumab trials completed, including long-term extension follow-up in SLE patients.
Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L, et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2550–7.
Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L, et al. An international cohort study of cancer in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(5):1481–90.
Disclosure
Dr. Askanase has served as a principal investigator for belimumab clinical trials.
Katrina Shum reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shum, K., Askanase, A. Belimumab and the Clinical Data. Curr Rheumatol Rep 14, 310–317 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-012-0264-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-012-0264-4