Abstract
Renal involvement in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in the form of severe lupus nephritis is associated with a significant burden of morbidity and mortality. Conventional laboratory biomarkers in current use have not been very successful in anticipating disease flares, predicting renal histology, or decreasing unwanted outcomes. Since early treatment is associated with improved clinical results, it is thus essential to identify new biomarkers with substantial predictive power to reduce the serious sequelae of this difficult to control lupus manifestation. Indeed, considerable efforts and progress have been made over the last few years in the search for novel biomarkers. Since urinary biomarkers are more easily obtainable with much less risk to the patient than repeat renal biopsies, and these may more accurately discern between renal disease and other organ manifestations than their serum counterparts, there has been tremendous interest in studying new candidate urine biomarkers. Below, we review several promising urinary biomarkers under investigation, including total proteinuria and microalbuminuria, urinary proteomic signatures, and the individual inflammatory mediators interleukin-6, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, CXCL16, IP-10, and tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron JS (1999) Lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:413–424
Ward MM (2000) Changes in the incidence of end-stage renal disease due to lupus nephritis, 1982-1995. Arch Intern Med 160:3136–3140
Ward MM (2009) Changes in the incidence of endstage renal disease due to lupus nephritis in the United States, 1996-2004. J Rheumatol 36:63–67
Esdaile JM, Joseph L, MacKenzie T, Kashgarian M, Hayslett JP (1994) The benefit of early treatment with immunosuppressive agents in lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol 21:2046–2051
Faurschou M, Starklint H, Halberg P, Jacobsen S (2006) Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis: diagnostic and therapeutic delay increases the risk of terminal renal failure. J Rheumatol 33:1563–1569
Oelzner P, Deliyska B, Funfstuck R, Hein G, Herrmann D, Stein G (2003) Anti-C1q antibodies and antiendothelial cell antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus-relationship with disease activity and renal involvement. Clin Rheumatol 22:271–278
Moroni G, Radice A, Giammarresi G et al (2009) Are laboratory tests useful for monitoring the activity of lupus nephritis? A 6-year prospective study in a cohort of 228 patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:234–237
Esdaile JM, Joseph L, Abrahamowicz M, Li Y, Danoff D, Clarke AE (1996) Routine immunologic tests in systemic lupus erythematosus: is there a need for more studies? J Rheumatol 23:1891–1896
Illei GG, Tackey E, Lapteva L, Lipsky PE (2004) Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. I. General overview of biomarkers and their applicability. Arthritis Rheum 50:1709–1720
Liu CC, Manzi S, Ahearn JM (2005) Biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus: a review and perspective. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17:543–549
Illei GG, Tackey E, Lapteva L, Lipsky PE (2004) Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus: II. Markers of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 50:2048–2065
Illei GG, Lipsky PE (2004) Biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 6:382–390
Zhang X, Jin M, Wu H et al (2008) Biomarkers of lupus nephritis determined by serial urine proteomics. Kidney Int 74:799–807
Balow JE (2005) Clinical presentation and monitoring of lupus nephritis. Lupus 14:25–30
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Yee CS, Farewell V, Isenberg DA et al (2007) British Isles Lupus Assessment Group 2004 index is valid for assessment of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 56:4113–4119
Siedner MJ, Christopher-Stine L, Astor BC, Gelber AC, Fine DM (2007) Screening for proteinuria in patients with lupus: a survey of practice preferences among American rheumatologists. J Rheumatol 34:973–977
Siedner MJ, Gelber AC, Rovin BH et al (2008) Diagnostic accuracy study of urine dipstick in relation to 24-hour measurement as a screening tool for proteinuria in lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol 35:84–90
Christopher-Stine L, Petri M, Astor BC, Fine D (2004) Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio is a reliable measure of proteinuria in lupus nephritis. J Rheumatol 31:1557–1559
Ginsberg JM, Chang BS, Matarese RA, Garella S (1983) Use of single voided urine samples to estimate quantitative proteinuria. New Eng J Med 309:1543–1546
Rodby RA, Rohde RD, Sharon Z, Pohl MA, Bain RP, Lewis EJ (1995) The urine protein to creatinine ratio as a predictor of 24-hour urine protein excretion in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. Am J Kidney Dis 26:904–909
Eknoyan G, Hostetter T, Bakris GL et al (2003) Proteinuria and other markers of chronic kidney disease: a position statement of the national kidney foundation (NKF) and the national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases (NIDDK). Am J Kidney Dis 42:617–622
Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E et al (2003) National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Int Med 139:137–147
Bauer JW, Baechler EC, Petri M et al (2006) Elevated serum levels of interferon-regulated chemokines are biomarkers for active human systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Med 3:e491
Liang MH, Schur PH, Fortin P et al (2006) The American College of Rheumatology response criteria for proliferative and membranous renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum 54:421–432
Leung YY, Szeto CC, Tam LS et al (2007) Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio in an untimed urine collection is a reliable measure of proteinuria in lupus nephritis. Rheumatol 46:649–652
Birmingham DJ, Rovin BH, Shidham G et al (2007) Spot urine protein/creatinine ratios are unreliable estimates of 24 h proteinuria in most systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis flares. Kidney Int 72:865–870
Hebert LA, Birmingham DJ, Shidham G, Rovin B, Nagaraja HN, Yu CY (2009) Random spot urine protein/creatinine ratio is unreliable for estimating 24-hour proteinuria in individual systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis patients. Nephron Clin Pract 113:c177–c182
Toto RD (2004) Microalbuminuria: definition, detection, and clinical significance. J Clin Hypertens 6:2–7
Christopher-Stine L, Siedner M, Lin J et al (2007) Renal biopsy in lupus patients with low levels of proteinuria. J Rheumatol 34:332–335
Batlle-Gualda E, Martinez AC, Guerra RA, Pascual E (1997) Urinary albumin excretion in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus without renal disease. Ann Rheumatic Dis 56:386–389
Valente de Almeida R, Rocha de Carvalho JG, de Azevedo VF et al (1999) Microalbuminuria and renal morphology in the evaluation of subclinical lupus nephritis. Clin Nephrol 52:218–229
Gunnarsson I, Sundelin B, Heimburger M et al (2002) Repeated renal biopsy in proliferative lupus nephritis–predictive role of serum C1q and albuminuria. J Rheumatol 29:693–699
Birmingham DJ, Rovin BH, Shidham G, Bissell M, Nagaraja HN, Hebert LA (2008) Relationship between albuminuria and total proteinuria in systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:1028–1033
Cottiero RA, Madaio MP, Levey AS (1995) Glomerular filtration rate and urinary albumin excretion rate in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nephron 69:140–146
Fine DM, Ziegenbein M, Petri M et al (2009) A prospective study of protein excretion using short-interval timed urine collections in patients with lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 76:1284–1288
James P (1997) Protein identification in the post-genome era: the rapid rise of proteomics. Q Rev Biophys 30:279–331
Schaub S, Wilkins J, Weiler T, Sangster K, Rush D, Nickerson P (2004) Urine protein profiling with surface-enhanced laser-desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Kidney Int 65:323–332
Wu T, Mohan C (2009) Proteomic toolbox for autoimmunity research. Autoimmun Rev 8:595–598
Suzuki M, Ross GF, Wiers K et al (2007) Identification of a urinary proteomic signature for lupus nephritis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 22:2047–2057
Suzuki M, Wiers K, Brooks EB et al (2009) Initial validation of a novel protein biomarker panel for active pediatric lupus nephritis. Pediatr Res 65:530–536
Uehara Y, Makino H, Seiki K, Urade Y (2009) Urinary excretions of lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase predict renal injury in type-2 diabetes: a cross-sectional and prospective multicentre study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:475–482
Mosley K, Tam FW, Edwards RJ, Crozier J, Pusey CD, Lightstone L (2006) Urinary proteomic profiles distinguish between active and inactive lupus nephritis. Rheumatol 45:1497–1504
Varghese SA, Powell TB, Budisavljevic MN et al (2007) Urine biomarkers predict the cause of glomerular disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:913–922
Oates JC, Varghese S, Bland AM et al (2005) Prediction of urinary protein markers in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 68:2588–2592
Lee P, Peng H, Gelbart T, Wang L, Beutler E (2005) Regulation of hepcidin transcription by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1906–1910
Wu T, Fu Y, Brekken D et al (2010) Urine proteome scans uncover total urinary protease, PGDS, SAP and SOD as potential markers of lupus nephritis. J Immunol. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900292
Dienz O, Rincon M (2009) The effects of IL-6 on CD4 T cell responses. Clin Immunol 130:27–33
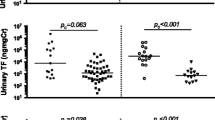
Li Y, Tucci M, Narain S et al (2006) Urinary biomarkers in lupus nephritis. Autoimmun Rev 5:383–388
Okada M, Kitahara M, Kishimoto S, Matsuda T, Hirano T, Kishimoto T (1988) IL-6/BSF-2 functions as a killer helper factor in the in vitro induction of cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol 141:1543–1549
Tanigawa T, Nicola N, McArthur GA, Strasser A, Begley CG (1995) Differential regulation of macrophage differentiation in response to leukemia inhibitory factor/oncostatin-M/interleukin-6: the effect of enforced expression of the SCL transcription factor. Blood 85:379–390
Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Heinrich PC (1988) Recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2/HSF) regulates the synthesis of acute phase proteins in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 232:347–350
Richards HB, Satoh M, Shaw M, Libert C, Poli V, Reeves WH (1998) Interleukin 6 dependence of anti-DNA antibody production: evidence for two pathways of autoantibody formation in pristane-induced lupus. J Exp Med 188:985–990
Iwano M, Dohi K, Hirata E et al (1993) Urinary levels of IL-6 in patients with active lupus nephritis. Clin Nephrol 40:16–21
Tesar V, Masek Z, Rychlik I et al (1998) Cytokines and adhesion molecules in renal vasculitis and lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:1662–1667
Tsai CY, Wu TH, Yu CL, Lu JY, Tsai YY (2000) Increased excretions of beta2-microglobulin, IL-6, and IL-8 and decreased excretion of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in urine of patients with active lupus nephritis. Nephron 85:207–214
Alon R, Kassner PD, Carr MW, Finger EB, Hemler ME, Springer TA (1995) The integrin VLA-4 supports tethering and rolling in flow on VCAM-1. J Cell Biol 128:1243–1253
McHale JF, Harari OA, Marshall D, Haskard DO (1999) TNF-alpha and IL-1 sequentially induce endothelial ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in MRL/lpr lupus-prone mice. J Immunol 163:3993–4000
Baran D, Vendeville B, Ogborn M, Katz N (2000) Cell adhesion molecule expression in murine lupus-like nephritis induced by lipopolysaccharide. Nephron 84:167–176
Wu T, Xie C, Bhaskarabhatla M et al (2007) Excreted urinary mediators in an animal model of experimental immune nephritis with potential pathogenic significance. Arthritis Rheum 56:949–959
Wu T, Xie C, Wang HW et al (2007) Elevated urinary VCAM-1, P-selectin, soluble TNF receptor-1, and CXC chemokine ligand 16 in multiple murine lupus strains and human lupus nephritis. J Immunol 179:7166–7175
Kiani A, Mohan C, Wu T, Madger L, Petri M (2009) VCAM-1 is a better measure of SLE renal activity than NGAL and CXCL16. Arthritis Rheum 60:S345
Ikeda Y, Fujimoto T, Ameno M, Shiiki H, Dohi K (1998) Relationship between lupus nephritis activity and the serum level of soluble VCAM-1. Lupus 7:347–354
Gough PJ, Garton KJ, Wille PT, Rychlewski M, Dempsey PJ, Raines EW (2004) A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 10-mediated cleavage and shedding regulates the cell surface expression of CXC chemokine ligand 16. J Immunol 172:3678–3685
Shimaoka T, Nakayama T, Fukumoto N et al (2004) Cell surface-anchored SR-PSOX/CXC chemokine ligand 16 mediates firm adhesion of CXC chemokine receptor 6-expressing cells. J Leukoc Biol 75:267–274
Minami M, Kume N, Shimaoka T et al (2001) Expression of scavenger receptor for phosphatidylserine and oxidized lipoprotein (SR-PSOX) in human atheroma. Ann NY Acad Sci 947:373–376
Chandrasekar B, Bysani S, Mummidi S (2004) CXCL16 signals via Gi, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, I kappa B kinase, and nuclear factor-kappa B and induces cell-cell adhesion and aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 279:3188–3196
Shimaoka T, Nakayama T, Kume N et al (2003) Cutting edge: SR-PSOX/CXC chemokine ligand 16 mediates bacterial phagocytosis by APCs through its chemokine domain. J Immunol 171:1647–1651
Teramoto K, Negoro N, Kitamoto K et al (2008) Microarray analysis of glomerular gene expression in murine lupus nephritis. J Pharmacol Sci 106:56–67
Luster AD (1998) Chemokines–chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Engl J Med 338:436–445
Neville LF, Mathiak G, Bagasra O (1997) The immunobiology of interferon-gamma inducible protein 10 kD (IP-10): a novel, pleiotropic member of the C-X-C chemokine superfamily. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:207–219
Shiozawa F, Kasama T, Yajima N et al (2004) Enhanced expression of interferon-inducible protein 10 associated with Th1 profiles of chemokine receptor in autoimmune pulmonary inflammation of MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R78–R86
Narumi S, Takeuchi T, Kobayashi Y, Konishi K (2000) Serum levels of ifn-inducible PROTEIN-10 relating to the activity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cytokine 12:1561–1565
Avihingsanon Y, Phumesin P, Benjachat T et al (2006) Measurement of urinary chemokine and growth factor messenger RNAs: a noninvasive monitoring in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 69:747–753
Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H et al (1997) TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:32401–32410
Meighan-Mantha RL, Hsu DK, Guo Y et al (1999) The mitogen-inducible Fn14 gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein that modulates fibroblast adhesion and migration. J Biol Chem 274:33166–33176
Maecker H, Varfolomeev E, Kischkel F et al (2005) TWEAK attenuates the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Cell 123:931–944
Wiley SR, Cassiano L, Lofton T et al (2001) A novel TNF receptor family member binds TWEAK and is implicated in angiogenesis. Immunity 15:837–846
Feng SL, Guo Y, Factor VM et al (2000) The Fn14 immediate-early response gene is induced during liver regeneration and highly expressed in both human and murine hepatocellular carcinomas. Am J Pathol 156:1253–1261
Campbell S, Michaelson J, Burkly L, Putterman C (2004) The role of TWEAK/Fn14 in the pathogenesis of inflammation and systemic autoimmunity. Front Biosci 9:2273–2284
Campbell S, Burkly LC, Gao HX et al (2006) Proinflammatory effects of TWEAK/Fn14 interactions in glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol 176:1889–1898
Gao HX, Campbell SR, Burkly LC et al (2009) TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) induces inflammatory and proliferative effects in human kidney cells. Cytokine 46:24–35
Molano A, Lakhani P, Aran A, Burkly LC, Michaelson JS, Putterman C (2009) TWEAK stimulation of kidney resident cells in the pathogenesis of graft versus host induced lupus nephritis. Immunol Lett 125:119–128
Morris SC, Cohen PL, Eisenberg RA (1990) Experimental induction of systemic lupus erythematosus by recognition of foreign Ia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 57:263–273
Reap EA, Sobel ES, Jennette JC, Cohen PL, Eisenberg RA (1993) Conventional B cells, not B1 cells, are the source of autoantibodies in chronic graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol 151:7316–7323
Zhao Z, Burkly LC, Campbell S et al (2007) TWEAK/Fn14 interactions are instrumental in the pathogenesis of nephritis in the chronic graft-versus-host model of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 179:7949–7958
Kaplan MJ, Ray D, Mo RR, Yung RL, Richardson BC (2000) TRAIL (Apo2 ligand) and TWEAK (Apo3 ligand) mediate CD4+ T cell killing of antigen-presenting macrophages. J Immunol 164:2897–2904
Kaplan MJ, Lewis EE, Shelden EA et al (2002) The apoptotic ligands TRAIL, TWEAK, and Fas ligand mediate monocyte death induced by autologous lupus T cells. J Immunol 169:6020–6029
Schwartz N, Su L, Burkly LC et al (2006) Urinary TWEAK and the activity of lupus nephritis. J Autoimmun 27:242–250
Schwartz N, Rubinstein T, Burkly LC et al (2009) Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 11:R143
Rovin BH, Zhang X (2009) Biomarkers for lupus nephritis: the quest continues. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1858–1865
Schwartz N, Michaelson JS, Putterman C (2007) Lipocalin-2, TWEAK, and other cytokines as urinary biomarkers for lupus nephritis. Ann NY Acad Sci 1109:265–274
Das L, Suzuki M, Devarajan P, Rovin B, Ying J, Brunner HI (2009) Candidate urinary biomarkers may predict histological features on lupus nephritis biopsy. Arthritis Rheum 60:S750
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reyes-Thomas, J., Blanco, I. & Putterman, C. Urinary Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 40, 138–150 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8197-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8197-z