Article Text
Abstract
Purpose Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex disorder with significant genetic underpinnings that are only partially explained by multiple genome-wide association studies (GWAS). It is possible that several loci of modest significance remain to be discovered.
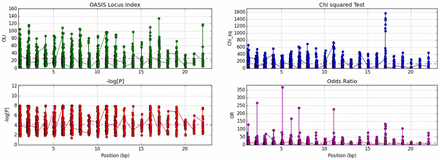
Methods GWAS meta-analyses of different populations teases out common loci. Moreover, association clustering methods such as gene- and locus-based tests are more powerful than single variant analysis for identifying modest genetic effects. Here, OASIS, a locus-based test, is applied to European (EU) and Chinese (Chi) GWAS to identify common significant non-HLA, autosomal genes/loci for SLE. OASIS was applied to six SLE dbGAP GWAS datasets, 4 EU and 2 Chi. Overall meta-analysis of 31,718 EU and 14,159 Chi subjects was performed. OASIS statistics used to identify significant loci included the novel OASIS locus index (OLI) defined as the product of maximum -logP at a locus with the ratio of actual to predicted number of significant SNPs. Chi-squared tests and odds ratios were also used to test the significance of loci.
Results Top non-HLA significant loci, common in both ethnicities were 2q32.2 (STAT4, rs11889341, P=10–65), 7q32.1 (IRF5, rs35000415, P=10–45) and 16p11.2 (ITGAM, rs1143679, P=10–47). Additionally, four loci strongly replicated in both ethnicities, identifying the known SLE genes: TNFSF4 (P=10–26), BANK1 (P=10–9), TNIP1 (P=10–17) and UBE2L3 (P=10–14). Other notable loci included 17p11.2 (TNFRSF13B (BLyS receptor), rs55701306, P=10–8, OR=14, OLI=66), 16p13.13 (CLEC16A, rs7186145, P=10–8, OR=9.7, OLI=54), 10q11.23 (WDFY4, rs1904605, P=10–7, OR=26, OLI=83) and 1q25.3 (NCF2, rs7552232, P=10–7, OR=42, OLI=89). Overall, OASIS identified 1488 modestly significant loci (P<10–8), of which 183 replicated in both ethnicities. This study will detail the results of these associated loci.
Conclusion Several genes and loci for SLE were identified using a cluster-based approach, OASIS, on six publicly available GWAS datasets from EU and Chi populations. This large meta-analyses will help comprehensive evaluation of SLE susceptibility genes.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.